Scientists develop corrosion-induced electrodes for biomass upgrading

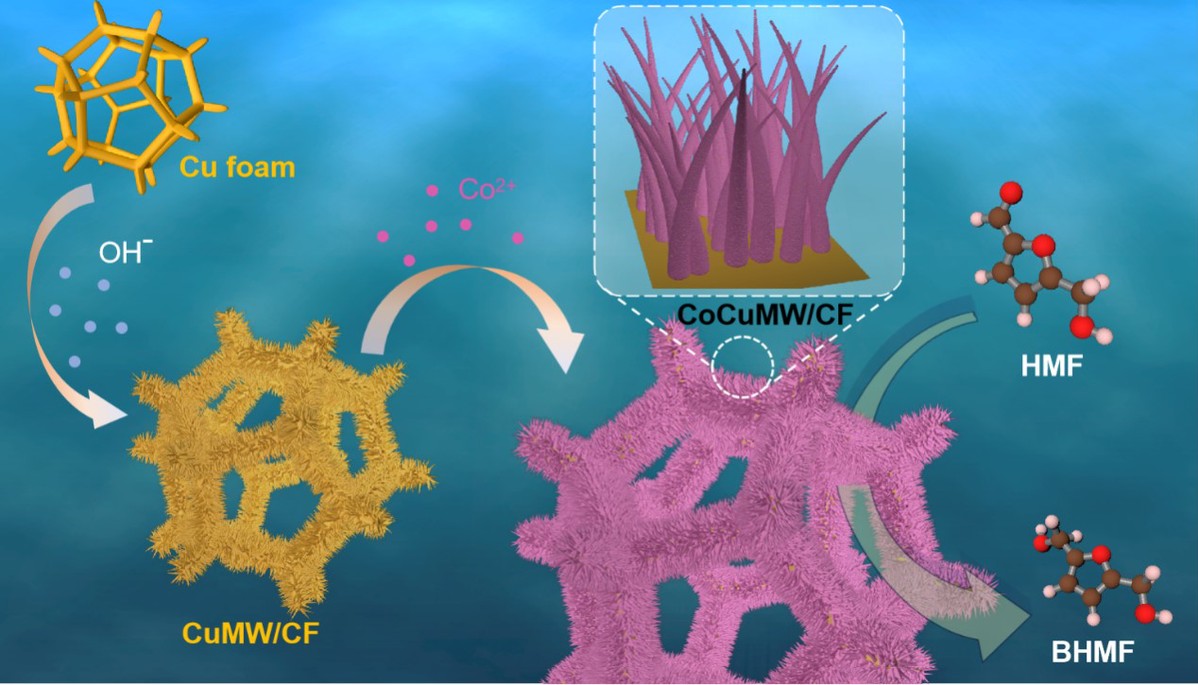
A research team led by Professor Zhang Jian from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has utilized metal corrosion to prepare high-performance electrodes, enabling efficient and cost-effective upgrading of bio-based 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). The study was published in Chem Catalysis.
Corrosion is a common phenomenon that can lead to material failure and economic losses. Meanwhile, researchers are exploring its potential for beneficial applications, particularly in biomass upgrading.
Biomass is among the most abundant renewable resources on earth. Through catalytic conversion, biomass can upgrade into fuels and chemicals that can substitute traditional fossil resources, thus playing an important role in achieving "peak carbon dioxide emission and carbon neutrality".
Inspired by the idea of "turning damage into benefits", researchers at NIMTE combined spontaneous metal corrosion with efficient biomass upgrading. They fabricated CoCu microwire arrays on copper foam (CoCuMW/CF) through cobalt ion-enhanced corrosion induction.
The CoCuMW/CF electrode enables efficient electrochemical reduction of HMF to 2,5-bis (hydroxymethyl) furan (BHMF), which can be further converted into environmentally friendly plastic or rubber products, high-value derivatives, and high-quality bio-based chemicals through simple methods.
Moreover, the prepared CoCuMW/CF electrode demonstrated a remarkable HMF conversion rate of 95.7% and a BHMF yield of 85.4% at the potential of -0.5 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE), indicating superior performance for HMF hydrogenation in a neutral electrolyte.
Notably, the activation energy for the HMF electrocatalytic reduction was 16.6 ± 2.5 kJ·mol-1, significantly lower than in thermocatalysis.
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that the CoCuMW/CF electrode exhibits reduced free energy barriers for both the initial and subsequent hydrogenation steps of HMF. This reduction in energy barriers enhances the catalytic performance and the selectivity for BHMF production.
The study challenges conventional views on corrosion phenomena and enables highly efficient electrochemical hydrogenation using copper-based electrocatalysts for biomass upgrading at extremely low cost. This advancement holds great promise for accelerating HMF electrohydrogenation applications.
- Interest in Turkiye soars among Chinese tourists after introduction of visa-free entry
- Yunnan e-bike fire probe identifies raft of failings
- Investigation report released on e-bike fire that killed 8 in Southwest China
- Understanding Xi's vision of China and the world through New Year message
- 'Artificial sun' experiment finds way to break plasma density limit
- China reports 20% rise in inter-regional trips on first day of holiday



































