Tapestries of history
The art of embroidery was an important part of a woman's education in China, at least until a few generations ago. Embroidered items also had a crucial role in rites and rituals, with carefully designed patterns that indicated rank and importance in the imperial courts, and differing degrees of respect for deities in religious ceremonies. In the courts, the embroidered panel in front of an official's robe would immediately identify his rank. Elaborate altar cloths in shrines and temples were a reflection of the congregation's devotion, and wealth. A daughter would be trained to sew, and embroider, as soon as she was old enough to hold a needle. Her embroidery would start with handkerchiefs, towels and pillowcases and expand to sheets, tablecloths, underwear and outer jackets that would slowly accumulate into an impressive dowry. Embroidery was also appreciated as an art, and various regions in China soon developed their unique styles, often as far back as earliest dynasties. Apart from Han embroidery, there were four other major styles from Suzhou, Guangdong, Sichuan and Hunan.
Su embroidery (Suxiu)
Known as the home of China's silk culture, Suzhou has always had a significantly developed silkworm farming culture thanks to its fertile land and mild climate - both forming a conducive environment for the growth of its own embroidered arts.
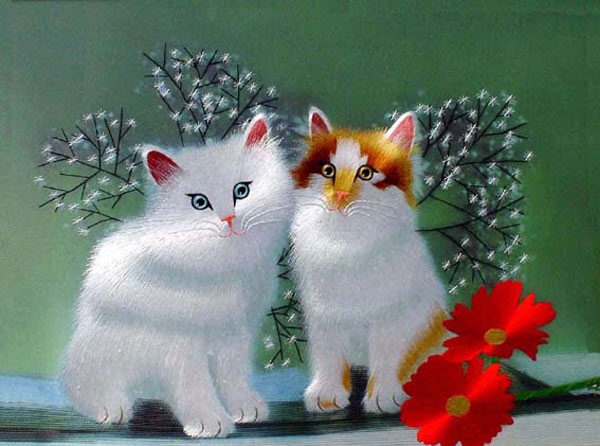 |
|
Su embroidery. Photos Provided to China Daily |
The earliest piece of Su embroidery was unearthed under the Ruiguang (Blessed Light) and Huqiu (Tiger Hill) towers built during the Northern Song Dynasty (AD 960-1127).
Historical records had it that Su embroidery was already widely applied on clothes during the Spring and Autumn Period (770-476 BC). By the Ming Dynasty (AD 1368-1644), raising silkworms and doing embroidery were common among "almost every country household".
Suzhou-style embroidery was also helped by the city's famous literati of the time, especially the Wu School of Painting, which offered pattern makers an inexhaustible source of inspiration.
Because of the cultured influences, Su embroidery has a refinement that is seldom found in embroidered works elsewhere.
Su embroidery enjoyed its heyday as the imperial courts showed continuous partiality toward its vivid style, particularly its depth and Su embroidery appeared on everyday items such as bedcovers, sachet, and bags for the scholar's fans.
At the present, the definition of Su embroidery has expanded to include works produced by Suzhou and its neighboring cities of Wuxi and Nantong, although embroidery produced in Suzhou still commands a higher price because of its perceived better value.
Yue embroidery (Yuexiu)
Among all the embroidery styles of China, the Guangdong style (Yue is the short term for Guangdong) may not be the best, but it is certainly the most special.
 |
| Yue embroidery |
It originated from the Li, an ethnic group that lives in the area, and the needlework is traditionally done by men.
Apart from its use of silk and floss, Guangdong embroidery is also known for its creative use of special materials such as peacock feathers and horsehair.
The earliest records of Guangdong embroidery can be traced back to the Tang Dynasty (AD 618-907) and it certainly flourished in the Ming Dynasty.
The largest piece of old Guangdong embroidery found by far is from the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), which measured 4.2 meters long and 2.8 meters wide.
Compared to Suzhou-style embroidery which was heavily influenced by literati's love of shanshui, or the paintings of mountains and rivers, Guangdong embroidery is more on the people's hope for prosperity and peace, hence the popularity of emblems such as the dragon and phoenix, bats, peaches and other auspicious symbols. In the same vein, the colors are brighter and the palette more varied.
It is said that this style was one of the first to travel overseas, when in 1514, during the Ming Dynasty, Portuguese merchants brought back some pieces as a tribute to their king.
Since then, Guangdong embroidery slowly accumulated an unexpected fan base overseas, mostly from the European courts, which began collecting the pieces.
During the Qing Dynasty, some British businessmen brought their clothes to Guangdong and had them embroidered, starting a trend in which local embroiderers started to incorporate Western-style designs into their pattern books. Exports boomed.
By the time of the Qing emperors Yongzheng and Qianlong from the mid-17th century to the late 18th century, there were workshops catering specifically to the export markets of Europe and the Middle East.